
From Legacy Systems to Cloud-Native Agility: How Cloud 9 Infosystems Accelerates AWS Modernization
Modernize legacy systems with AWS—secure, scalable, and cloud-native solutions by Cloud 9 Infosystems.

Cloud 9 delivers solutions and strategies to help you modernize critical legacy applications while reducing the cost to keep them running, allowing you to redeploy resources toward revenue-generating innovation.
With Cloud 9’s deep application development expertise on the cloud, we can partner with you to build applications in a PaaS- first model. Add to it our concurrent engineering philosophy and achieve results.
Small-medium businesses can now compete with larger Enterprises in developing custom B2B products & Enterprise Applications for Web & Mobile, at a rapid pace, yet at a fraction of the cost.
Our clients benefit from:
Azure provides all the on-demand backend Infrastructure, completely managed by Microsoft (be it Azure AD Services for identity, App Services, SQL/noSQL databases, Media services, Mobile services or Scheduler services), to automatically scale up and down and meet the ever-changing market needs.
We can help you with product selection, migration, application monitoring and maintenance, security and much more to help you deploy and integrate new cloud apps into your work environment.
Define and create comprehensive security infrastructure for all levels and types of cloud services, including security policies and procedures in place for controlling access to provider and customer systems.
We will work with you to design an identity management strategy with role-based access control and authentication, create operational policies and procedures to ensure integrity of your data.
Our Services:
Design and implement secure, highly-available, performant and resilient network design solutions.
Integrate with your existing IT environment through the largest network of secure private connections, hybrid database, storage solutions, data residency and encryption features — so your assets stay right where you need them.
Our Services:
Using Azure ARM model and Cloud 9’s teams onboarding strategy provides a rapid activation path based on best practices so you can build an operational, scalable and secure cloud environment. The service offers your teams the support they need from planning and implementation to knowledge transfer and closure.
Our Services:
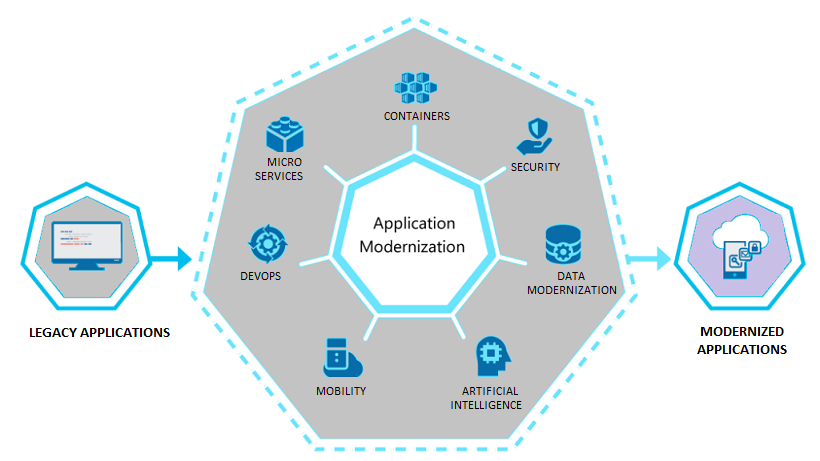
Our customers are integrating security, compliance and monitoring into DevOps workflows to ship cloud applications faster. Gain confidence to run cloud-native workloads in production. We help enterprises scale their ability to build and deliver quality cloud applications using DevOps and Continuous Delivery models with elastic, on-demand, agile infrastructure and services on Microsoft Azure.
Faster time to market
Real time monitoring
Reduced need for infrastructure support by your staff.
Code analysis to introduce minimal change to design cloud native application.
Tailor made workshops and discovery sessions that last 1-2 days, guiding our clients on strategy and approach towards implementing or transitioning towards Microservices architectures, Container & Serverless implementations, and DevOps- driven software development processes.
Join our “Envisioning Microservices Architecture” workshop to create an actionable plan for breaking up existing tiered or monolithic software into Microservices or even developing new software. Outcomes of the workshop include:
Our “Cloud Native App Assessment Sessions” help understand how and where to use a combination of Containers, Serverless computing and Azure Cloud services to develop secure, scalable and high-performance apps. Outcomes include:
Our comprehensive “Azure” DevOps Assessment and Planning” workshop is intended to assess suitability of existing development processes to support transition to Azure Dev Ops hosted environment, including:
As a Microsoft Gold Partner, we have deep knowledge of Microsoft 365 and can be your single source for purchasing, billing, deploying, managing and supporting Microsoft solutions.
SUCCESS STORIES
Modernization in Action
Organizations are modernizing applications to improve agility, scalability, and long-term performance. Explore our case studies to see how enterprises approach cloud and technology transformation.

Modernize legacy systems with AWS—secure, scalable, and cloud-native solutions by Cloud 9 Infosystems.

Cloud cost optimization is now a strategic priority for IT leaders. Discover proven best practices to reduce cloud spend by 20–30%, improve cost visibility, and maintain performance across AWS, Azure, and multi-cloud environments.
Discover how Azure AI Foundry enables enterprises in India to operationalize AI agents securely, govern them effectively, and scale AI without compliance risk.
Error: Contact form not found.
